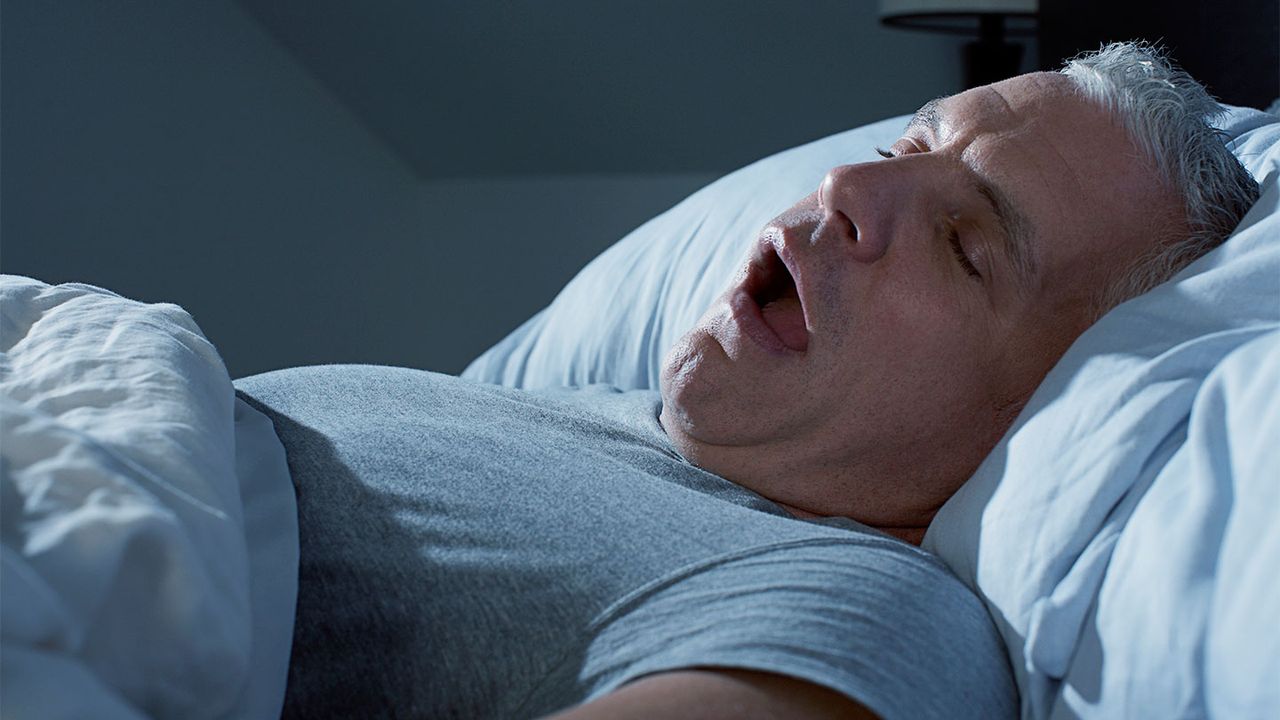
Although Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been consistently linked to chronic pain and other health conditions, but do we have any evidence linking OSA to gout? Let’s find out!
Understanding what Gout is.
Hyperuricemia, often known as increased blood uric acid levels, is the root cause of gout produce by sleep apnea. This results in the formation of urate crystals – the aggravating factor in gout pain and inflammation. The uric acid your body produces as a byproduct of regular bodily processes is considered harmless and non-threatening. It’s not bad for you in moderation, but too much can be dangerous.
Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, which are found in many different meals.
Excess uric acid in the body can build up and form sharp urate crystals in joints or tissue, but generally uric acid dissolves in the blood and exits the body through the urine. The inflammation and agony caused by these crystals in the joints is known as gout.
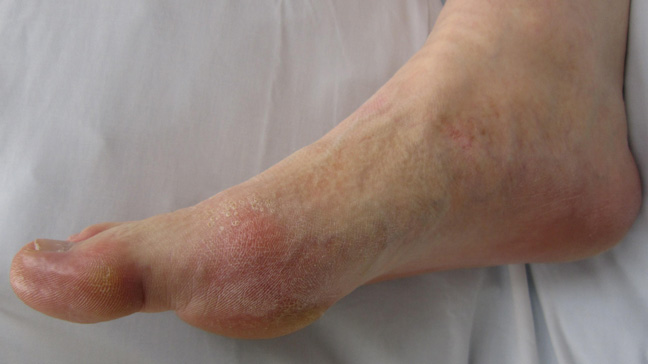
Symptoms of Gout
Nighttime attacks of gout are common and might come on suddenly. The following are some of the possible symptoms:
- Pain that persists long after a gout attack has subsided
- Extreme pain in the joints, most often the big toes but sometimes the fingers, wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles.
- Redness, pain, and swelling around the injured joint(s)
Gout Predisposing Factors
If you have more than one of the following characteristics, your risk of gout increases:
Gout often affects males between the ages of 30 and 50, and it is more common in men than in women. Gout is also more common among postmenopausal women. A lot of the things you eat are high in purines, which we’ll talk about in a minute.
Causes of gout include:
- A history of gout in the family
- Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus, Congestive Heart Failure, and Metabolic Syndrome
Untreated gout can cause joint damage or destruction, and it can also increase your chance of developing kidney stones. Disease of the kidneys, decreased renal function, or impaired renal function can all contribute to the development of gout. However, gout treatment can reduce the frequency of bouts and perhaps eliminate the ailment altogether.
A Possible Link Between Sleep Apnea and Gout
If you’ve been following our site for any length of time, or if you’ve read this post, you likely have a solid grasp on the basics of sleep apnea and its effects on health.
Although we won’t be covering obstructive sleep apnea in depth here, if you’re interested in learning more about the illness after reading about how it affects gout, you may want to check out our blog posts on Sleep Apnea Diagnosis and Treatment.
Sleep apnea and gout have been associated in several studies, although sleep apnea does not cause gout. Since your circadian cycle may affect your gout attacks, and nocturnal gout flares are likely to impact your sleep quality, there is a link between sleep and gout as well.
Patients with gout often reported symptoms such as insomnia, restless legs syndrome, and obstructive sleep apnea, according to research published in BMC Rheumatology.

However, the good news is that sleep apnea treatment can also aid in the treatment of other illnesses you may be experiencing. A CPAP machine is a great tool for treating sleep apnea.
Treatment with a CPAP Machine
One of the most prevalent and productive treatments for sleep apnea is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine therapy. The CPAP machine treatment maintains your airways open by providing a continual stream of air, allowing you to breathe better and preventing apnea.
One should not take their ability to breathe well at night for granted. Sleeping in an oxygen-rich environment has been linked to improved health and a reduced risk of developing a variety of conditions.
So how exactly does gout treatment with a CPAP machine work? Though further study is needed to confirm this, it has been hypothesised that treating sleep apnea, which causes low oxygen levels, may also help lower the increased uric acid levels that can lead to gout. If you suffer from sleep apnea, this may help alleviate your symptoms or prevent future attacks of gout.
Additional complications might arise from low oxygen levels elevating the heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar. Because of this, the CPAP machine is useful for treating not only sleep apnea but also other disorders including high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
Ways to Reduce Gout Pain and Get Some Rest
Symptoms of gout might make it difficult to sleep even in the absence of sleep apnea. Here are five things you may do to control your gout and get a good night’s rest.
Exercise
To put it simply, being overweight increases your chances of developing gout. Moderate exercise is beneficial for many health issues, including depression. Dropping several pounds and getting your body mass index down to normal limits may do wonders.
By reducing stress and opening airways, regular exercise is an effective treatment for sleep disturbances. Your symptoms may improve significantly if you walk or do yoga for 30 minutes every day. If you’re boosting your exercise levels, it may assist. Keep at it and pay attention to your body so you can avoid harm.
Improve Your Diet
Gout risk is increased when a person’s diet contains a high quantity of purine-rich foods. Foods high in purines include a few of the following:
- Beer and other alcoholic beverages
- Meats high in iron and zinc, such as red meat and organ meats
- Tuna, trout, anchovies, and sardines, together with other seafood
- Scallops and mussels are two examples of shellfish.
- Beverages sweetened with fruit sugars— such fructose or high fructose corn syrup— including soda or fruit juices

You don’t have to remove these foods from your diet altogether, but decreasing your intake can help prevent flare-ups. On the other hand, if consuming any of these foods brings on an acute episode of gout, you may want to cut it out of your diet.
Consuming a diet rich in fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grains, plant-based proteins, and low-fat dairy products can aid in the management of gout. One further thing that can assist is reducing consumption of processed foods.
Medication
Medications are useful for both reducing the severity of attacks and avoiding future attacks of gout. Common medications for gout include the uric acid-lowering drugs allopurinol and febuxostat, the anti-inflammatory drugs colchicine and corticosteroids, and the pain relievers aspirin and acetaminophen.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen, available without a prescription and over-the-counter, can alleviate the pain and inflammation associated with gout episodes and even shorten them.
See your doctor if you feel like you may benefit from taking medication to manage your gout. Never change the dosage or duration of your prescribed medicine without first speaking with your doctor.
Keep a Journal of Your Triggers
Many people get gout episodes whenever they eat certain foods. The ability to identify and prevent the causes of gout attacks is a powerful tool for managing the condition. Keep a mental or written record of the kinds of meals and beverages that trigger an exacerbation of your symptoms. Other frequent causes of gout are:
- Flare-ups are more common when the body is under stress from things like injury, sickness, or surgery.
- High blood pressure, heart disease, renal disease, and diabetes can all increase your risk for gout; if you have any of these problems, managing them can reduce your gout symptoms.
- Aspirin and some diuretics used to treat hypertension are two examples of drugs that might bring on an episode of gout.
More to read: The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Alzheimer’s Disease
